Brain trauma related SURGERIES
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) can result from accidents, falls, or blunt force trauma, leading to skull fractures, hematomas, and increased intracranial pressure. Surgical intervention is often necessary to relieve pressure, repair damage, and prevent permanent neurological deficits. MVD is a microsurgical procedure designed to relieve pressure on the trigeminal nerve caused by a nearby blood vessel. By carefully separating the nerve from the compressing vessel, this surgery can provide long-term relief while preserving nerve function.
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) can result from accidents, falls, or blunt force trauma, leading to skull fractures, hematomas, and increased intracranial pressure. Surgical intervention is often necessary to relieve pressure, repair damage, and prevent permanent neurological deficits. MVD is a microsurgical procedure designed to relieve pressure on the trigeminal nerve caused by a nearby blood vessel. By carefully separating the nerve from the compressing vessel, this surgery can provide long-term relief while preserving nerve function.
Brain Trauma Surgeries
Types of Brain Trauma Surgeries
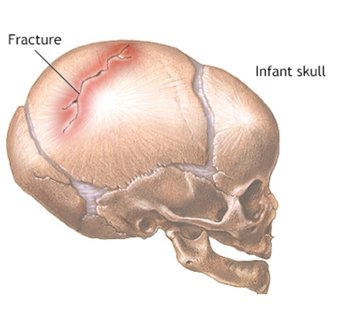

Skull Fracture Repair
1. Required when bone fragments are displaced or pressing on the brain.
2. Involves lifting depressed fragments and securing them with plates, screws, or wires.
3. Protects the brain, restores skull integrity, and prevents infection.

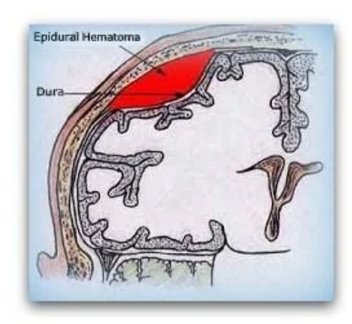
Extradural Hematoma (EDH) Evacuation
1. EDH is bleeding between the skull and dura mater, often caused by trauma.
2. Rapid blood accumulation can compress brain tissue and increase intracranial pressure.
3. Surgery involves incision, removal of the hematoma, and repair of damaged vessels to relieve pressure.
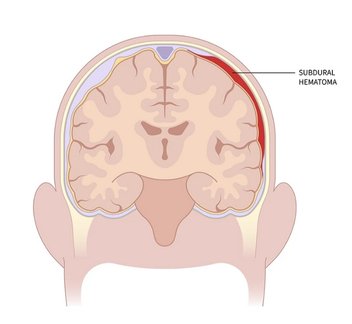

Subdural Hematoma (SDH) Evacuation
1. SDH occurs between the dura and arachnoid membranes, usually from torn bridging veins.
2. Surgery includes craniotomy, hematoma drainage, and sometimes removal of the outer hematoma capsule to prevent recurrence.
3. Relieves pressure and supports neurological recovery.
Why Choose Surgery for Brain Trauma
Prevents permanent neurological damage by relieving intracranial pressure.
Restores skull integrity and protects the brain from further injury.
Reduces risk of complications, including seizures, infection, or cognitive deficits.
Supports faster recovery and improved long-term outcomes.
Personalized care with expert neurosurgical planning and postoperative monitoring.
FAQs
Surgery is indicated for displaced skull fractures, large EDH/SDH, increased intracranial pressure, or neurological deterioration.
Yes, children with traumatic brain injuries can safely undergo surgery, with techniques tailored to pediatric patients.
Based on imaging (CT/MRI), injury severity, location of hematoma or fracture, and overall patient<br> health.
Hospital stay usually ranges from 1–2 weeks, with rehabilitation extending for weeks or months depending on severity.
Most patients gradually return to daily activities, although full recovery depends on injury severity and rehabilitation.
Get Expert Surgical Care for Traumatic Brain Injuries
Consult Dr. Sachin Ashokrao Giri for advanced brain trauma surgeries to protect neurological function and optimize recovery.

